With reference to assignments 8 and 9, what characteristics does an analyst (you) examine when evaluating DFD quality? (1500 words)
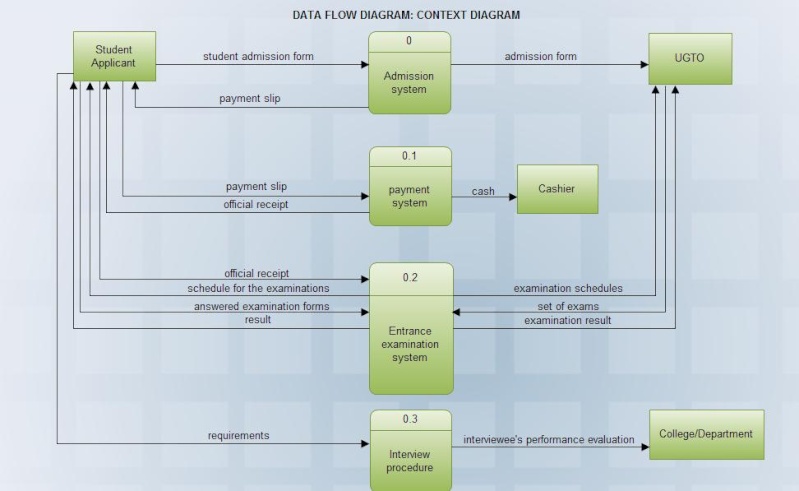
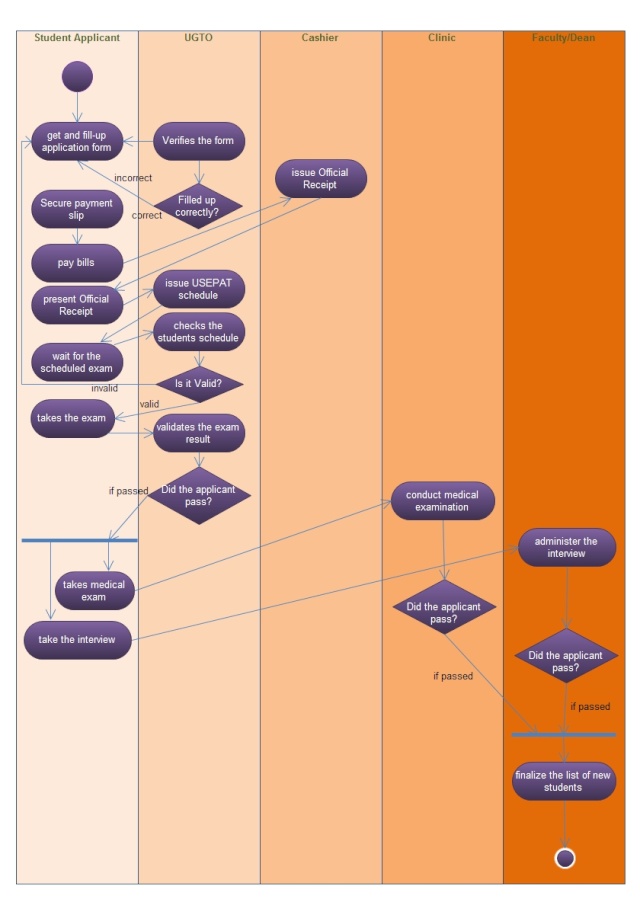
Both assignment eight and nine are based on making UML or Unified Modeling Language. In assignment 8, it is about constructing an activity diagram of the pre-enrolment system in continuation of the previous assignment. As what I have defined activity diagram in my previous post, Activity Diagrams are typically used for business process modeling, for modeling the logic captured by a single use case or usage scenario, or for modeling the detailed logic of a business rule. Creating activity diagrams are very useful in describing the flow control of the target system. It is also helpful in determining the use cases and the business processes of a firm. According to IBM, Activity diagrams are useful in modeling a system in a simple and intuitive illustrations or figures of what happens on the workflow and the activities can be done in parallel or multiple way and it illustrates to verify whether there are alternative paths through the workflow. The next assignment is an exercise o developing a Data Flow Diagram (DFD) of the pre-enrolment system. The data flow diagram, from the word itself, shows the flow of data from external entities into the system, how the data moved from one process to another and as well as its logical storage (Scott W. Ambler). It is a graphical illustration of the movement of data between the external entities and the different processes and data stores within a system. As an analyst, data flow diagram is a great help because it enable us to understand deeply the system. Base on the slide presentation of Jeffrey A. Hoffer, Joey F. George and Joseph S. Valacich entitled Structure System Requirements: process modeling, there are two defined data flow diagrams, includes context diagram and level-O diagrams. To differentiate, context diagram is a data flow diagram (DFD) of the scope of an organizational system that shows the system boundaries external entities that interact with the system and the major information flows between the entities and the system. On the other hand, level-O diagram is a data flow diagram (DFD) that simply represents a system’s major processes, data flows and data stores at a high level detail.
If we will try to compare the two, they are almost similar. Both diagrams are designed to illustrate a process modeling. The only difference that I have observed is that activity diagram is used for process modeling through describing the flow of the target system while data flow diagrams shows the flow of data from external entities into the system. UML activity diagrams are somewhat considered as the object-oriented equivalent of flow charts and data flow diagrams (DFDs) from structured developments. Both diagrams are useful in determining the flow of the data, entities and even the system itself.
Now, back to the main question, what characteristics does an analyst (you) examine when evaluating DFD quality? To be honest, I really had a hard time thinking of how to create good and perfect data flow diagrams. And in fact, there are different types of DFDs that can be used in modeling the process of a system. Here are some of the characteristics:

 Posted by
Posted by